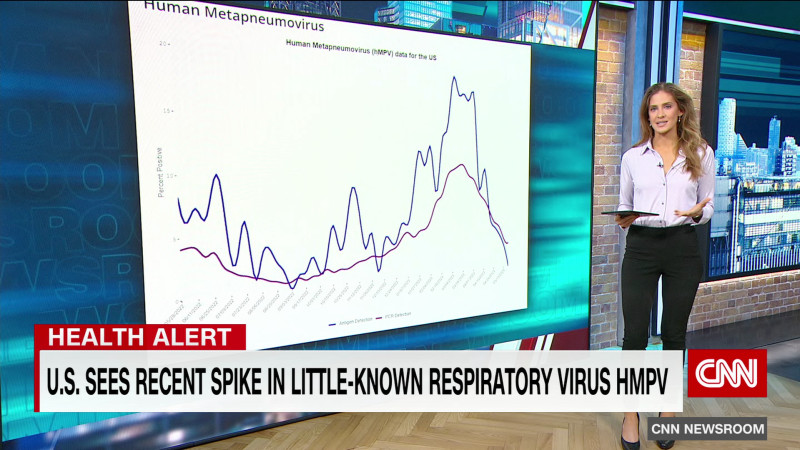
HMPV Virus: A Growing Global Concern
As reports of a surge in Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) cases emerge from China and other parts of the world, fears of another global pandemic are rising. The virus, first identified in 2001 in the Netherlands, is a respiratory infection that causes flu-like symptoms, primarily affecting young children, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. The similarities to COVID-19's spread and symptoms, despite the lack of an HMPV vaccine, is causing significant alarm.
Understanding HMPV: Symptoms and Transmission
HMPV is a member of the same family as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and its spread is similar to other viral respiratory infections. It’s typically spread through close contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated surfaces. The symptoms mirror those of the common cold and flu: runny nose, coughing, fever, congestion, sore throat, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to bronchitis or pneumonia. The incubation period, the time between exposure and the appearance of symptoms, is typically three to six days.
Serious Symptoms to Watch For
While most HMPV infections are mild, some individuals may experience more serious complications. These include:
- Severe difficulty breathing
- Dehydration
- Worsening of underlying respiratory conditions
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you or someone you know experiences any of these serious symptoms.
Global Response to the HMPV Outbreak
The recent increase in HMPV cases, particularly in China, has prompted several countries to take precautions. Nigeria, for instance, is implementing measures to quarantine travelers arriving from high-risk areas for two to three days. These measures, including testing at points of entry, are aimed at preventing the spread of the virus. While the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Africa Centre for Disease Control haven't yet issued formal alerts, the situation is closely monitored. Several countries like Malaysia and India have already issued health advisories and are enhancing surveillance measures.
India's Response to HMPV Cases
India, too, has reported HMPV cases, prompting various states to issue guidelines. Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Delhi are implementing strategies to prepare for a possible surge in respiratory illnesses. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is continuously tracking trends, emphasizing that HMPV is not a new virus and that many in the population likely have immunity. The response in India highlights a proactive approach to contain the spread and mitigate potential health challenges.
HMPV vs. COVID-19: Key Differences
Although HMPV shares similarities with COVID-19 in terms of symptoms and transmission, there are crucial differences. HMPV is a seasonal virus, typically appearing during winter and spring, unlike COVID-19, which has demonstrated cyclical patterns throughout the year due to the emergence of new variants. Importantly, there is no antiviral therapy or vaccine available for HMPV, unlike COVID-19, for which multiple vaccines and treatments exist. Furthermore, studies indicate a potential correlation between the relaxation of COVID-19 prevention measures and a subsequent increase in HMPV cases. The decreased exposure to various respiratory illnesses during strict COVID-19 restrictions appears to have impacted the rate of HMPV infection.
The Road Ahead: Prevention and Preparedness
While panic is unwarranted, vigilance is essential. Simple preventive measures, such as frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, and maintaining good hygiene, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Maintaining adequate ventilation in indoor spaces can also help to limit transmission. Although there's no specific HMPV vaccine, the treatments focus on managing the symptoms. Staying informed about the latest developments and adhering to public health advisories are crucial steps in mitigating the potential impact of HMPV.
A Measured Response
The current situation highlights the importance of strong public health infrastructure and international cooperation. The global community must learn from the COVID-19 pandemic and apply these lessons to effectively address emerging infectious disease threats. While the rise of HMPV cases is concerning, a measured, data-driven response, coupled with effective public health measures, can help to minimize its impact and prevent a widespread outbreak. The collective effort to mitigate risks, combined with readily available information, plays a pivotal role in safeguarding global health and wellbeing. Learning from the lessons of past outbreaks and understanding the dynamics of respiratory viruses is paramount in safeguarding global health. The emphasis on preventing the spread of misinformation and maintaining a calm and reasoned approach is a key factor in maintaining public health during this time.