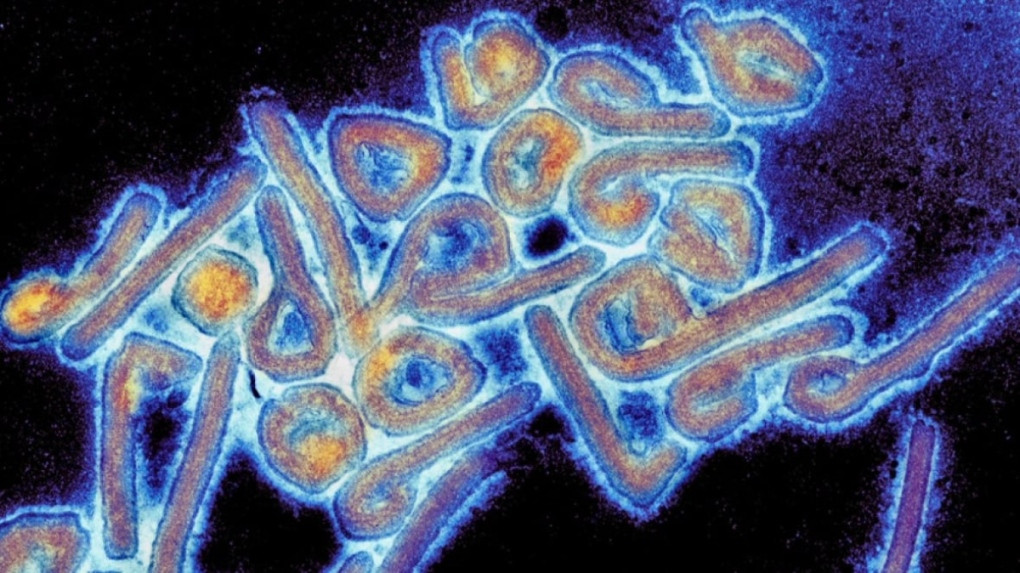
A Deadly Hemorrhagic Fever Emerges in Rwanda
Rwanda is facing its first outbreak of the Marburg virus, a rare but deadly hemorrhagic fever that has claimed the lives of nine people. This outbreak has become the fourth largest Marburg outbreak ever recorded, prompting global concern and raising questions about the potential for further spread.
The Marburg Virus: A Close Relative to Ebola
Marburg virus is a member of the Filoviridae family, the same family as Ebola. It is a highly virulent virus with a fatality rate of up to 88%, making it a serious public health threat. The virus is typically found in fruit bats and can be transmitted to humans through contact with infected bats or their bodily fluids. Human-to-human transmission can also occur through direct contact with the bodily fluids of an infected individual. The Marburg virus causes a hemorrhagic fever, which is characterized by fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and bleeding.
Why Is This Outbreak a Cause for Concern?
The current outbreak has several factors that have raised concerns among health experts:
1. Rapidly Increasing Case Count
The rapid increase in the number of cases in Rwanda, reaching over 27 within a short period, suggests that the virus may have been circulating for some time without detection. This indicates a potential for widespread transmission and underscores the importance of early detection and response.
2. Significant Number of Healthcare Workers Infected
The fact that a substantial percentage of the Marburg patients in Rwanda are healthcare workers is particularly concerning. This suggests a potential for nosocomial transmission, meaning the virus is spreading within healthcare facilities. This highlights the need for strict infection control measures and the proper use of protective gear by medical personnel.
3. Outbreak in a Well-Connected Region
The outbreak has already been detected in several districts of Rwanda, including the capital city of Kigali. This raises concerns about the potential for the virus to spread to other regions and countries through human travel. The case of a traveler who came into contact with a Marburg patient in Rwanda and subsequently traveled to Belgium serves as a reminder of the global interconnectedness and the potential for rapid transmission.
Global Response and Challenges
The World Health Organization (WHO) has deemed the risk of this outbreak as “very high at the national level, high at the regional level and low at the global level.” Several countries are taking steps to prevent the spread of the virus, including monitoring travelers from Rwanda, providing support to Rwandan health authorities, and raising awareness among healthcare professionals. However, several challenges remain in the fight against this deadly virus:
1. Lack of Vaccines and Treatments
Currently, there are no approved vaccines or treatments specifically for Marburg virus disease. This makes supportive care, such as providing fluids and managing symptoms, the primary treatment option. The lack of targeted therapies underscores the need for ongoing research and development to find effective solutions.
2. Limited Resources in Some Regions
The lack of sufficient resources and healthcare infrastructure in some regions, including parts of Africa, can hinder the ability to detect and respond to outbreaks effectively. This can lead to delayed diagnoses, increased transmission, and a higher risk of mortality.
3. Potential for Misdiagnosis and Delayed Treatment
The initial symptoms of Marburg virus can mimic those of other common illnesses, which can lead to misdiagnosis and delayed treatment. This can exacerbate the severity of the illness and increase the risk of transmission to others.
What Can We Do?
While the global community mobilizes to combat this outbreak, it’s important to be aware of the risks and take preventative measures:
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest information and guidelines from health authorities.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after contact with potentially contaminated surfaces or bodily fluids.
- Limit Exposure: Avoid contact with sick individuals or their bodily fluids.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you develop any of the symptoms of Marburg virus, seek immediate medical attention.
As the global community works to contain this outbreak, the focus remains on effective surveillance, rapid response, and the development of vaccines and treatments to prevent future outbreaks. While there are no guarantees, we can hope for a swift containment of the virus in Rwanda and the prevention of further spread.
The Future: A Race Against Time
The Marburg virus outbreak in Rwanda serves as a stark reminder of the ongoing threats posed by emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. While scientists continue to research and develop vaccines and treatments, the need for robust surveillance, public health preparedness, and global collaboration remains paramount to effectively prevent and respond to these threats.