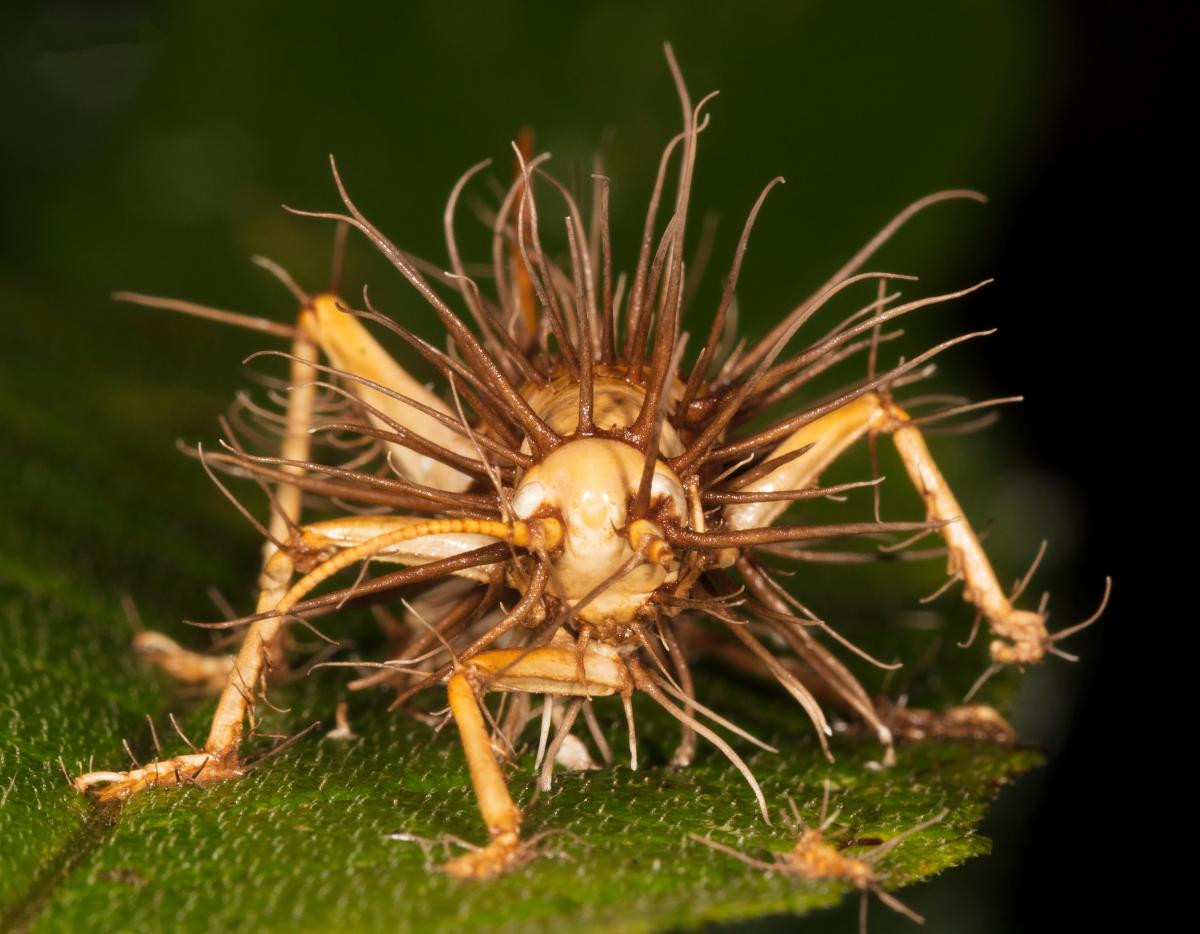
A wildlife researcher working in the Peruvian Amazon stumbled upon a dead tarantula infected by 'zombie fungus' and captured the nightmarish sight on video. The zombie fungus, formally known as Cordyceps, seizes control of the mind and motor functions of its host before eating away at its body and sprouting from within.
'It took over his nervous system and forced him to come to this location, said wildlife researcher Chris Ketola, who posted the video on his Instagram.
'And then as he died, the fungus sprouted out of his body, allowing the spores to spread to another unsuspecting tarantula.'
If this sounds familiar, it's because Cordyceps was the inspiration for the hit video game and TV drama The Last of Us, in which humans struggle to survive after an infectious fungus begins turning people into zombies.
'This is a truly horrific but also incredible thing for our our team to have found tonight,' Ketola said.
When an insect host becomes infected with Codryceps, the fungus begins draining its body of nutrients - feeding on the insect from within.
Next, it fills the host's body with spores that will allow the fungus to reproduce, then hacks into the insect's mind.
The Cordyceps spores compel the insect to move to a higher location where more sunlight and warmth create the perfect conditions for the fungus to reproduce.
When the host finally dies, the fungus bursts forth from its body and releases more spores that will infect more insects.
Scientists aren't sure exactly how Cordyceps manages to take over its host's mind and motor functions.
Cordyceps, also known as the zombie fungus, was the inspiration for hit video game and drama series The Last of Us. But don't worry - this fungus can't actually infect humans.
But recent studies have detected chemical signals from the fungi inside infected insects. Some of these signals, which are likely secreted proteins, may target the host's behavioral systems
In The Last of Us, a fictitious, mutated form of Cordyceps infects and takes over the minds of humans, turning them into violent zombies.
But in real-life, Cordyceps can't infect people.
Each one of these fungal species are highly specialized, meaning that they've evolved to only infect a few select hosts.
Some fungal pathogens can make the transition from animals to humans, but Cordyceps is not one of them, experts say.
What is the Zombie Fungus?
Cordyceps is a genus of fungi that primarily attacks invertebrates by slowly consuming their bodies. The most well-known Cordyceps species is Cordyceps militaris, which infects caterpillars. Cordyceps militaris is known for its bright orange fruiting body, which emerges from the caterpillar's body.
How Does the Fungus Infect its Hosts?
Cordyceps spores infect their hosts by landing on their bodies and penetrating the cuticle, or exoskeleton. The spores then grow into hyphae, which are long, thread-like structures that invade the host's tissues. The hyphae eventually reach the host's brain, where they release chemicals that control the host's behavior.
The Fungus's Devious Plan: Turning its Host Into a Zombie
Once the fungus has taken control of the host's brain, it manipulates the host to move to a location that is favorable for the fungus's growth and reproduction. This location is typically a high, humid, and well-lit area. For example, the zombie-ant fungus will force its host to climb to the top of a plant.
The infected insect will then remain there, often with its mandibles clamped onto a leaf or twig. This ensures that the fungus can spread its spores to other insects when the host dies.
The Real-Life Zombie Fungus Isn't As Scary As in The Last of Us
While the zombie fungus is a fascinating and terrifying example of nature's power, it is important to note that it is not as dangerous as it is portrayed in the popular video game and TV show 'The Last of Us'.
In the game and show, a mutated form of Cordyceps infects humans and turns them into zombies. This is a fictional scenario, and there is no evidence that Cordyceps can infect humans.
A World of Strange and Wonderful Creatures: Exploring the Nature of the Amazon
Ketola's discovery of a Cordyceps-infected tarantula in the Peruvian Amazon highlights the diversity of life in this incredible ecosystem. The Amazon rainforest is home to millions of species of plants and animals, many of which are still unknown to science.
The Amazon is also a region that is under increasing threat from deforestation and climate change. As we continue to learn more about the Amazon's biodiversity, it is important to protect this vital ecosystem for future generations.