California Wildfires Fueling Soil Erosion, Threatening Water Resources
The threat of wildfires in California extends far beyond the immediate devastation. A recent study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface has uncovered a concerning consequence of these fires: widespread soil erosion that jeopardizes water resources and flood safety.
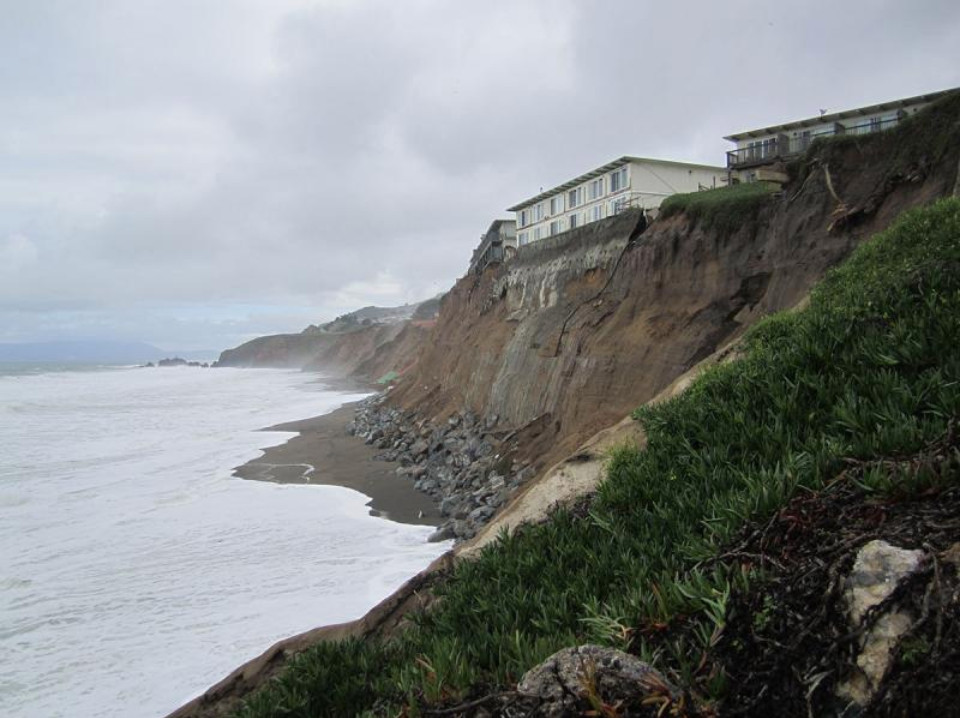
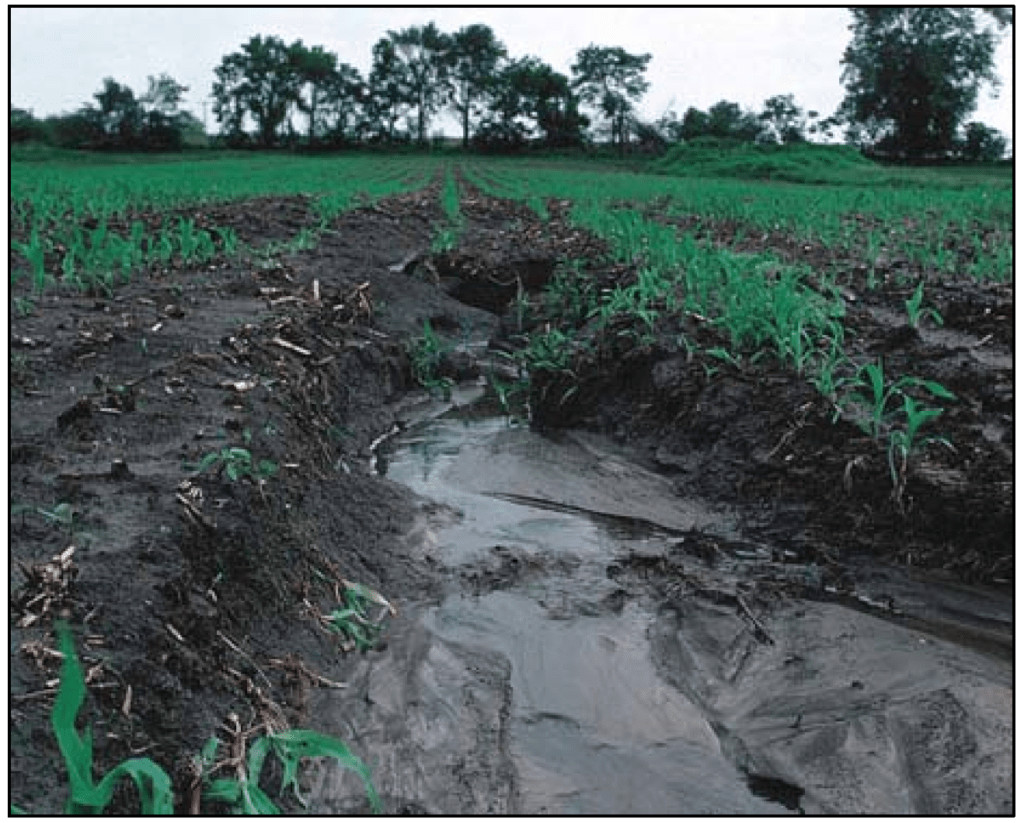
The research, spanning from 1984 to 2021, revealed a staggering amount of soil erosion resulting from wildfires. Millions of tons of eroded soil, known as sediment, have been washed into streams and rivers, eventually reaching reservoirs. This alarming trend has far-reaching implications for a state already grappling with water scarcity.
Sediment Accumulation: A Threat to California's Water Supply
As reservoirs fill with sediment, their capacity to capture and store water diminishes. This poses a significant challenge for California, a state grappling with a persistent drought. The reduced storage capacity could exacerbate water shortages and undermine efforts to manage the ongoing drought.
Increased Flood Risk: The Downstream Consequences of Erosion
The surge in sediment load in rivers and streams increases the risk of flooding in downstream communities. The eroded soil, carried by water currents, can block waterways, reducing their capacity to handle water flow during heavy rainfall events. This can lead to localized flooding, damaging infrastructure and posing risks to human safety.
A Vicious Cycle: Wildfires, Erosion, and Sedimentation
The interconnected cycle of wildfires, erosion, and sedimentation is a growing concern in California. As climate change fuels more frequent and intense wildfires, the likelihood of severe soil erosion increases. This creates a feedback loop where wildfires exacerbate erosion, and erosion, in turn, can make landscapes more susceptible to future wildfires.
The Urgency of Addressing Post-Fire Sediment Mobilisation
The study underscores the critical need for effective management strategies to mitigate the detrimental impacts of post-fire sediment mobilization. State officials face a daunting task in addressing this multifaceted problem.
Potential Solutions: A Balancing Act
The study suggests several potential solutions, including more frequent dredging of reservoirs to remove accumulated sediment and implementing erosion control measures in areas affected by wildfires. However, these approaches come with substantial financial and logistical challenges.
Looking Ahead: A Complex Challenge
As California navigates the complexities of a changing climate, tackling the issue of post-fire sediment mobilization is crucial for safeguarding water resources and protecting communities from flood risks. The findings of this study illuminate the interconnected nature of environmental challenges in the face of climate change. It emphasizes the need for proactive strategies to mitigate the consequences of wildfires and safeguard the state's water infrastructure and ecosystems for future generations.
A Call for Action: From Research to Reality
The research serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of environmental challenges. It is not enough to simply study the problem; action is needed to mitigate the consequences of wildfires and protect California's vital water resources. This requires a concerted effort from policymakers, scientists, and communities alike to implement effective solutions and ensure the long-term sustainability of the state's water infrastructure and ecosystems.