The Global E-Waste Crisis: A Growing Problem with Huge Potential
The world is increasingly reliant on technology, and with that comes a growing problem: e-waste. E-waste, or electronic waste, encompasses discarded electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and refrigerators. It is a complex issue with environmental, economic, and social implications. This article will delve into the current state of the global e-waste market, exploring the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
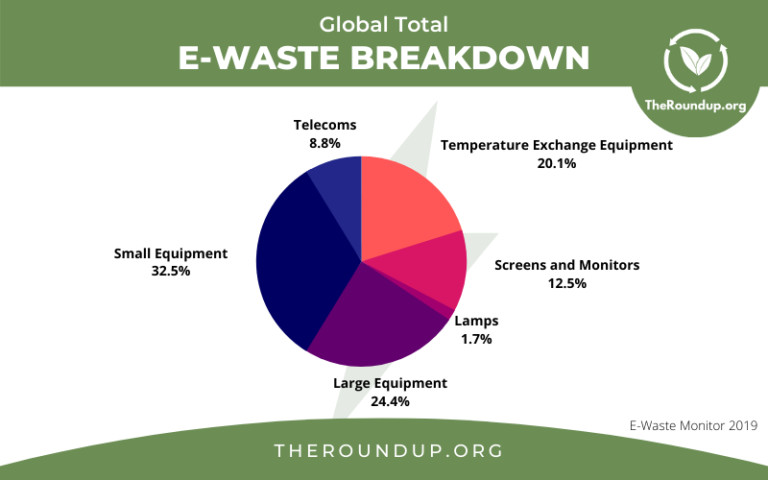
The Growing E-Waste Mountain: A Global Challenge
The e-waste problem is rapidly escalating. According to the Global E-waste Monitor 2020, the world generated 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, and this figure is projected to reach 74.7 million metric tons by 2030. The United States, China, and India are among the top e-waste generators globally, with a significant proportion originating from discarded mobile phones, laptops, and other personal electronics.
The environmental impact of e-waste is substantial. Electronic devices contain hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into the environment and cause soil and water contamination. Improper e-waste disposal can also lead to the release of greenhouse gases, further contributing to climate change.
The E-Waste Market: A Potentially Lucrative Solution
While e-waste presents a pressing environmental challenge, it also presents a significant economic opportunity. The global e-waste management market is estimated to be worth over $114.5 billion by 2031. This growth is driven by several factors, including increasing electronic device production, stricter regulations on e-waste disposal, and rising consumer awareness of the environmental impact of e-waste.
The Challenges of E-Waste Management
Despite the lucrative nature of the e-waste market, there are significant challenges in effectively managing e-waste. One of the primary challenges is the lack of proper infrastructure and regulations in many countries. In developing nations, e-waste is often managed in informal and unregulated sectors, leading to health and environmental hazards.
The lack of awareness among consumers about responsible e-waste disposal practices is another challenge. Many people are unaware of the risks associated with improper e-waste disposal, leading to an increased burden on the environment. Additionally, the complex nature of e-waste, with its diverse components and hazardous materials, makes it difficult to process and recycle effectively.
Global Collaboration and Regulatory Frameworks
Addressing the e-waste crisis requires a collaborative approach involving governments, businesses, and consumers. Governments play a vital role in enacting policies and regulations that promote responsible e-waste management. These regulations can include extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for their products' end-of-life management.
International organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) are working to address the global e-waste challenge. They provide technical assistance and capacity-building support to developing countries to establish robust e-waste management systems.
The Future of E-Waste: A Sustainable Path Forward
The future of e-waste management hinges on embracing circular economy principles. This approach emphasizes reducing, reusing, and recycling electronic products to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Innovation and Technology
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in improving e-waste management. Advanced sorting technologies enable efficient separation of valuable materials from e-waste, increasing recycling rates. Researchers are also developing new methods for extracting valuable metals from e-waste, further reducing reliance on virgin materials.
Consumer Awareness and Behavior Change
Shifting consumer behavior is essential for a sustainable e-waste future. Consumers can play a crucial role by buying products with longer lifespans, choosing products made with recycled materials, and properly disposing of their old electronics.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Collaboration between stakeholders is vital for a successful e-waste management strategy. Partnerships between manufacturers, recyclers, and government agencies are crucial for developing innovative solutions and improving overall e-waste management practices.
Conclusion: A Sustainable Future for Our Digital Age
E-waste is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. By implementing robust regulations, promoting innovation, raising consumer awareness, and fostering collaboration, we can pave the way for a more sustainable future for our digital age. The e-waste market holds immense potential, not only for economic growth but also for environmental protection. By embracing the opportunities presented by this sector, we can work towards a world where electronic waste is no longer a problem but a resource for a more sustainable future.