Hempcrete, a bio-based building material, has emerged as a sustainable alternative to traditional bricks and concrete, both of which contribute significantly to environmental degradation. Composed of hemp shiv—the dried inner core of the hemp plant—mixed with water and lime, hempcrete offers a lower environmental footprint compared to conventional materials.
The use of hempcrete in construction dates back over 1,500 years. Hemp plaster from the 6th century can still be found in the UNESCO-listed Ellora Caves in India. Additionally, hemp mortar was discovered in the ancient Merovingian bridge struts in France. In the 1980s, France led the modernization of hempcrete, casting it onsite in a manner similar to concrete.
However, mixing hempcrete correctly proved challenging for laypeople. An imbalance of ingredients could result in either a weak, runny mixture or a crumbly product. Moreover, drying times are lengthy—four to six weeks under favorable conditions and up to six months in colder, damp climates—limiting its widespread use, particularly in northern Europe.
Despite these challenges, hempcrete’s eco-friendly properties have driven its integration into the construction industry. Unlike conventional crops, hemp requires minimal fertilizers and pesticides, grows rapidly, and can be densely planted, providing natural weed control.
While hempcrete production consumes energy, it offers a virtually unlimited lifespan compared to synthetic wall infills and insulation. Additionally, its primary ingredient—hemp—is a renewable resource that requires significantly less energy and carbon during production. Efforts in France and Belgium during the early 2000s sought to overcome the barriers preventing hempcrete from achieving widespread use.
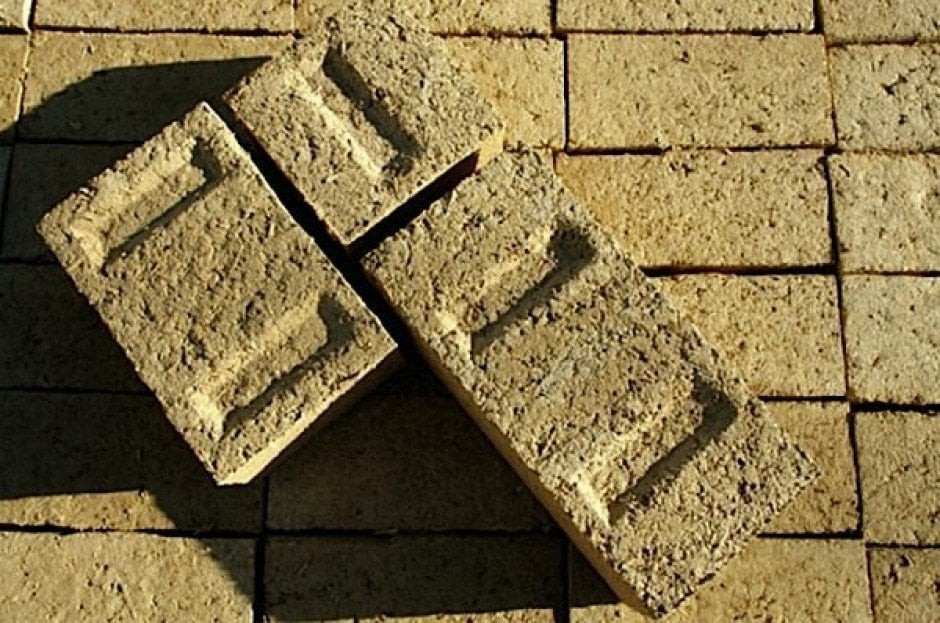
A breakthrough came with the development of the hempcrete block, or "green brick," which removed the need for specialized skills and guesswork in hempcrete applications. This lightweight, fibrous block maintains hempcrete’s sustainability benefits while expanding its practical use.
Free of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the green brick retains hempcrete’s moisture absorption, acoustic insulation, and thermal conduction properties. Its lightweight, consistent design makes it easy to transport and deploy on construction sites without the need for specialized training, increasing its market potential.
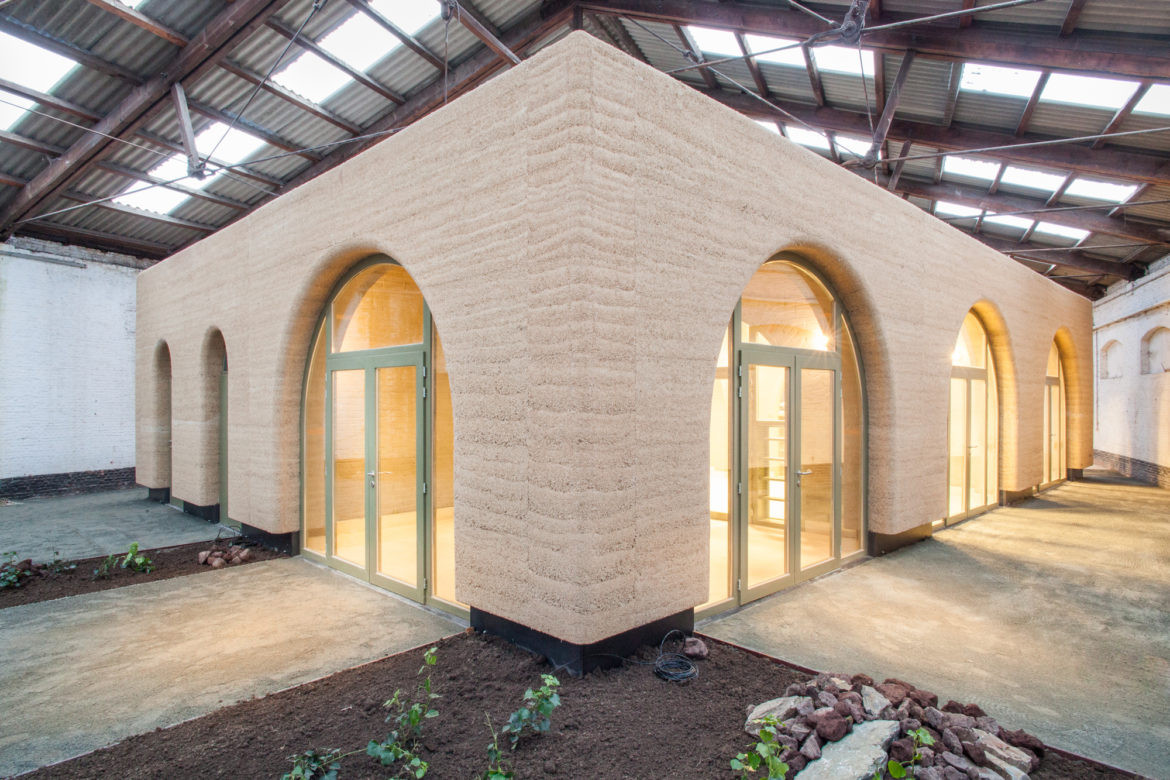
Concrete is a reinforced structural material capable of supporting itself, whereas hempcrete is typically used as insulation around wooden, concrete, or steel frames. However, hempcrete blocks can support themselves, making them suitable for multi-story buildings.
Most applications in countries like South Africa, the Netherlands, and France showcase hempcrete's use around a supporting frame. Research continues to enhance hempcrete’s structural properties by adjusting its composition to match the strength of conventional materials while retaining its eco-friendliness. This research has become even more relevant in the post-pandemic world, where homes now serve as living and working spaces.
Unlike synthetic insulation materials like fiberglass and polyurethane, which quickly heat up and cool down, hempcrete provides better thermal performance. It heats gradually and retains warmth longer through a process known as decrement delay, making it ideal for homes that require efficient heating during colder months.
Europe has become a hub for hempcrete production, with the material widely used to retrofit older structures and as a core component in new builds across France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, and Italy. Although the UK has lagged behind, with 300-400 hempcrete homes built, it is quickly catching up.
IsoHemp, a Belgian company founded in 2011, has become a key player in the hempcrete industry. Operating in five countries, it produces over a million hempcrete blocks annually and claims its projects save around 18,000 tons of CO2 per year.
The future of hempcrete construction is expected to focus on prefabrication, using modular approaches similar to timber-framed houses. In the UK, companies are building homes with hempcrete that resemble conventional estate houses but offer significantly better environmental performance. Retrofitting pre-1940s housing stock, which is often inefficient and leaky, is also gaining traction.
Although hempcrete’s full potential has yet to be realized, its innovative applications are gaining attention. For instance, BMW uses lightweight hemp polymer in the doors of its i3 electric cars. In southern Italy, hempcrete is being used in earthquake-prone areas as a flexible material that can withstand seismic movements, offering a more resilient alternative to concrete. These applications highlight hempcrete’s potential as a leading material in sustainable construction.
Hempcrete: A Greener Future for Construction
Liam Donohoe, a lecturer in Engineering at Technological University Dublin, believes that hempcrete is well-positioned to address the global housing needs. He emphasizes the importance of integrating hempcrete with modern technologies and construction methods. This includes modular housing concepts, passive house design, and integrating with smart energy technologies.
Donohoe also highlights the importance of standardization and certification for hempcrete. He argues that robust certification is essential to give architects and professionals the confidence to specify hempcrete in their projects. This involves comprehensive testing, data collection, and adherence to established standards.
While hempcrete faces challenges in the form of drying times and the need for specialized skills, the green brick innovation has overcome some of these barriers. The green brick is easier to use and more adaptable to the current construction cycle.
Hempcrete: A Game Changer in Sustainable Construction
As awareness of climate change grows, the demand for sustainable building materials is increasing. Hempcrete, with its low carbon footprint, renewable resources, and superior insulation properties, is poised to become a major player in the construction industry. With continued research and development, hempcrete could revolutionize construction and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
The use of hempcrete in construction is a promising development in the move toward a more sustainable future. While the material faces challenges in drying times and specialized skills, its benefits in terms of sustainability and performance are undeniable. As research and development continue, hempcrete is likely to become a mainstream material in the construction industry.