The Rise of In Situ Hybridization: A Revolution in Molecular Diagnostics
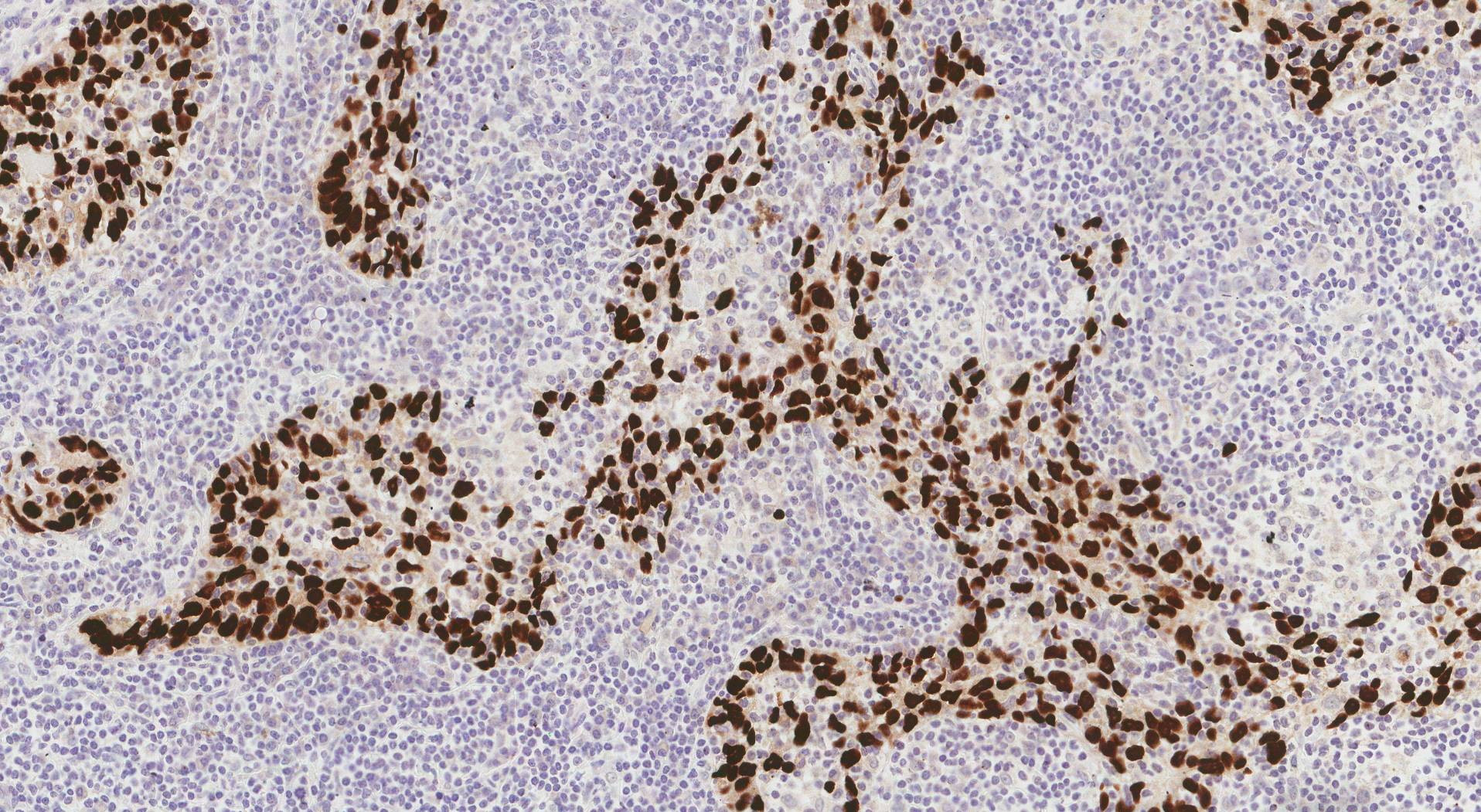
In Situ Hybridization (ISH) is a powerful molecular biology technique that has gained immense traction in recent years, particularly in the field of diagnostics. This technique allows scientists and researchers to visualize and analyze the presence and distribution of specific DNA or RNA sequences within cells and tissues. The ability to pinpoint the exact location of these sequences within the intricate biological landscape has revolutionized our understanding of various diseases, paving the way for more targeted and personalized treatments.
The Underlying Principles and Applications of ISH
ISH relies on the principle of complementary base pairing, a fundamental concept in molecular biology. The technique involves using short, single-stranded DNA or RNA probes labeled with a detectable marker, such as a fluorescent dye or an enzyme, to hybridize with their complementary target sequences within the sample. The probe binds to the target sequence, creating a detectable signal that can be visualized under a microscope or other imaging techniques.
The applications of ISH are extensive and span diverse fields:
- Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: ISH plays a crucial role in identifying specific genes or mutations associated with various types of cancer, helping in accurate diagnosis and predicting the likelihood of disease progression. For instance, ISH can detect HER2 gene amplification in breast cancer, which helps determine the appropriate treatment strategy.
- Infectious Disease Detection: ISH is used to diagnose and monitor infectious diseases by detecting specific viral or bacterial DNA or RNA sequences within infected tissues. This technique is particularly useful in identifying pathogens in challenging cases where traditional methods might fall short.
- Neurobiology Research: ISH has emerged as an indispensable tool in neuroscience research, enabling scientists to study the expression of genes and the distribution of specific RNA molecules within the brain. This has provided valuable insights into brain development, neurodegenerative disorders, and the intricacies of neuronal function.
- Forensic Science: ISH has found applications in forensics, helping to identify individuals from biological samples, such as blood or tissue, by analyzing unique DNA sequences.
The Market Dynamics of the In Situ Hybridization Industry
The global In Situ Hybridization (ISH) market is on a trajectory of rapid growth, driven by several key factors:
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in ISH technology, such as the development of automated systems, advanced probes, and improved imaging techniques, have significantly enhanced the sensitivity, speed, and reliability of this technique.
- Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases: The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders, has fueled the demand for accurate and timely diagnostics, leading to a surge in the adoption of ISH.
- Growing Investments in R&D: Significant investments in research and development in the biotechnology and pharmaceuticals sectors have led to the development of new ISH-based diagnostic tests and therapeutic agents, further propelling market growth.
Key Players and Market Trends in the In Situ Hybridization Industry
The ISH market is a vibrant landscape, with several key players contributing to its growth and evolution. These players include:
- Abbott Laboratories: Abbott is a leading provider of in vitro diagnostics and molecular diagnostics, including ISH-based assays.
- Leica Microsystems: Leica Microsystems is a renowned manufacturer of microscopes and imaging systems, offering a range of products and solutions for ISH applications.
- Agilent Technologies: Agilent Technologies is a global leader in life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets, with a strong portfolio of ISH products and services.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific: Thermo Fisher Scientific is a global provider of scientific research, analysis, and diagnostics solutions, including a broad range of ISH reagents and instruments.
Future Outlook: The Potential of In Situ Hybridization
The future of ISH looks promising, with several emerging trends poised to shape the industry:
- Development of Multiplex ISH: Multiplex ISH techniques are gaining traction, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple target sequences in a single sample. This capability offers greater insights into the complex interplay of genes and biological processes.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the analysis of ISH data, facilitating more accurate and efficient interpretation of results.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: The ISH market is expanding into emerging markets, driven by increasing awareness and adoption of advanced diagnostic tools.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Scientific Advancements and Healthcare
In Situ Hybridization has undoubtedly emerged as a powerful tool for scientific advancements and healthcare. Its ability to precisely visualize and analyze target sequences within cells and tissues has revolutionized our understanding of biology, disease, and diagnostics. The ongoing development of new technologies and the expansion of its applications in diverse fields promise a bright future for ISH, ensuring its continued impact on research, healthcare, and beyond.