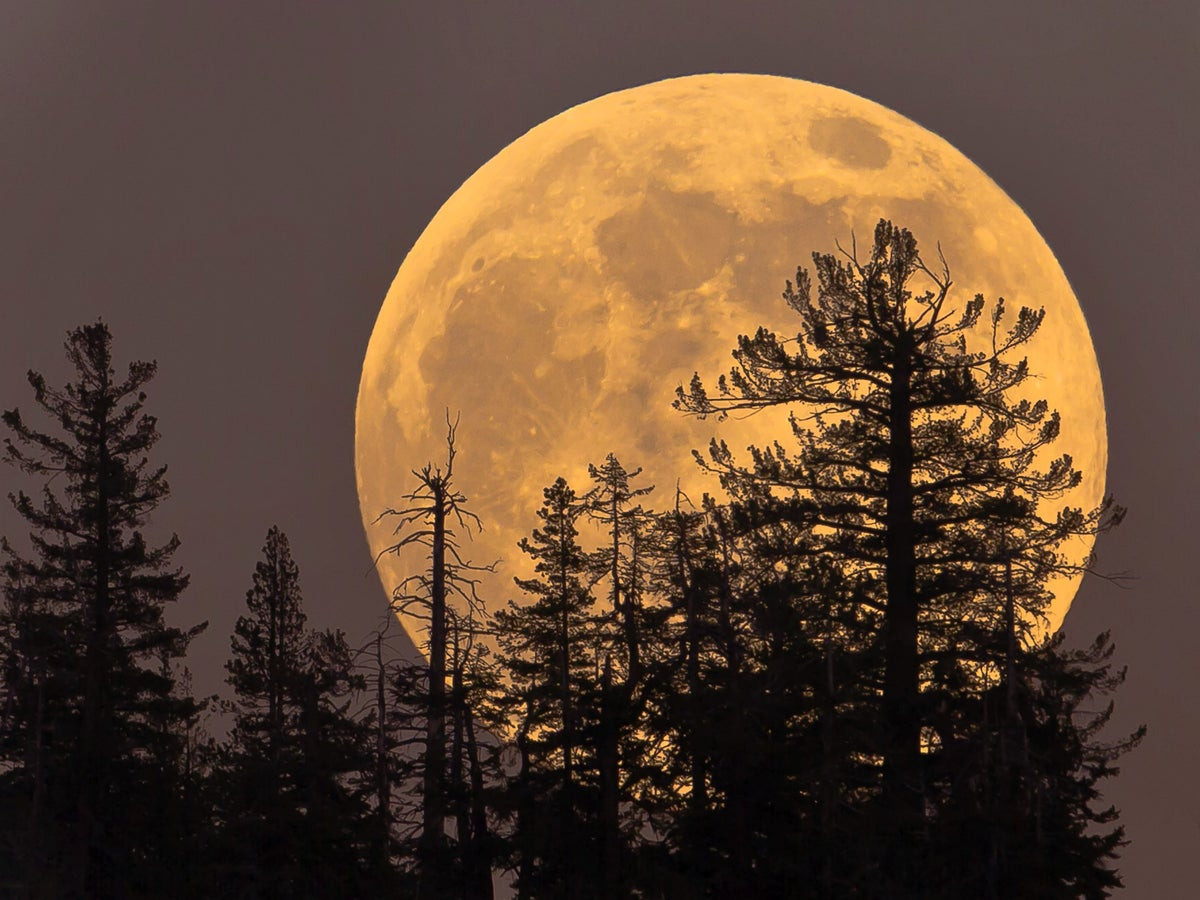
Two rare night sky sights make for an autumn treat today (Oct. 17). October's full Hunter's Moon, the largest supermoon of 2024, will rise in the sky opposite the bright comet C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan-ATLAS). The moon officially becomes full today (Oct. 17) at 7:26 a.m. EDT (1126 GMT), but it will appear full to the naked eye all throughout the night.
The Hunter's Moon of October 2024 will be the largest full moon of the year thanks to its proximity to Earth. The moon arrived at perigee, its closest point to Earth in its slightly elliptical, or oval-shaped orbit, on the evening of Wednesday (Oct. 16), coming within just 221,938 miles (357,174 kilometers) of our planet.
The result is that the Hunter's Moon is what is colloquially known as a "supermoon," meaning it appears roughly 14% larger than normal in the sky. Because the moment of full moon phase and perigee occurred within just hours, October's supermoon will be the largest of 2024.
Tonight, the moon will rise in the east just as the sun sets. Because full moons occur when the moon and sun are opposite one another with Earth in the middle, full moons always rise in the east just as the sun sets in the west.
Catching a Glimpse of the Hunter's Supermoon
The Hunter's supermoon was beginning to set at Chicago's O'Hare International Airport in the 5 a.m. hour Wednesday, and was visible Wednesday night and overnight into Thursday. It's set to reach peak illumination at 6:26 a.m. Thursday over clear skies.
"When the leaves fall and the deer fatten, it's time to hunt!" NBC 5 Meteorologist Alicia Roman said, of the name "Hunter's Moon."
According to the Royal Museums Greenwich, the “Hunter’s Moon” was named by Native Americans, so named because it gives hunters longer periods of night with which to stalk prey during the fall months.
Other cultures have named the moon the “Travel Moon” and the “Dying Grass Moon,” according to the website.
Why is the Hunter's Moon So Special?
According to NASA scientists, the moon will reach perigee, its closest point to the Earth on its orbit around the planet, on Wednesday night.
Approximately 11 hours later, the full moon will occur at approximately 6:26 a.m. Thursday, making the moon appear brighter and larger than normal.
According to experts, a “supermoon” occurs when the moon is within 90% of its closest approach distance to Earth. That distance is roughly 221,938 miles, according to NASA.
A “supermoon” appears slightly larger in the sky and a good deal brighter than a moon at apogee, or its furthest point from the Earth in its orbit. According to the Adler Planetarium, a “supermoon” can appear up to 30% brighter and 15% bigger than a “micromoon.”
This month’s “supermoon” is one of four straight the Earth is experiencing, but it ultimately will be the closest in calendar year 2024.
The Science Behind the Supermoon
The names of full moons are derived from the almanac, a reference book published regularly since the 18th century. The almanac, in turn, cites traditions of Native Americans, Colonial America and other North American-centered sources passed down through generations. The hunter's moon in October was so named for the time of year when hunters began collecting wild game, like deer, to store for the cold winter months. Game animals are typically fattened up to prepare themselves for the season.
The earliest recorded mention of "hunter's moon" was in 1710 in the Oxford English Dictionary.
The next full moon — the Beaver moon — will occur Nov. 15.
The full moon falls in the midpoint of the lunar cycle when the Earth is positioned directly between the sun and the moon. The moon takes about 30 days to orbit the Earth, which is the full lunary cycle.
When the moon’s orbit brings it closer to Earth than usual, the cosmic combo is called a supermoon. A supermoon occurs when the moon’s orbit is closest to Earth at the same time the moon is full. This happens when the full moon falls at perigee — its closest point to Earth in its orbit. Perigee is when the moon is 221,519 miles from Earth and appears bigger and brighter than a normal full moon.
When the moon reaches apogee, it’s at its farthest from Earth, a distance of 252,712 miles. If a full moon occurs while the moon is at apogee, it is called a micromoon.
Don't Miss Out on the Cosmic Show!
The Hunter's full moon, a supermoon, first rose in the sky Wednesday morning. According to the Adler Planetarium in Chicago, it's the "closest full supermoon" of the year.
"Last month’s full moon was about 223,000 miles away from Earth, which is considerably closer than the average Earth-to-Moon distance of 239,000 miles—making it a supermoon," the Adler said. "This month’s full Moon will get even closer to Earth than last month’s."
The Adler added that a full supermoon is estimated to appear "up to 30 percent brighter and nearly 15 percent bigger than a full moon" at its farthest from Earth.
If you're looking to get a closer view of the full moon, comets or any other night sky objects, our best telescopes for beginners guide can help you find what you need. And if something more portable is your preference, check our our best binoculars guide.