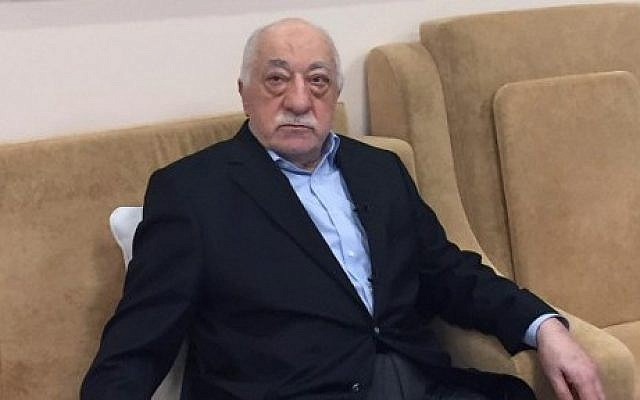
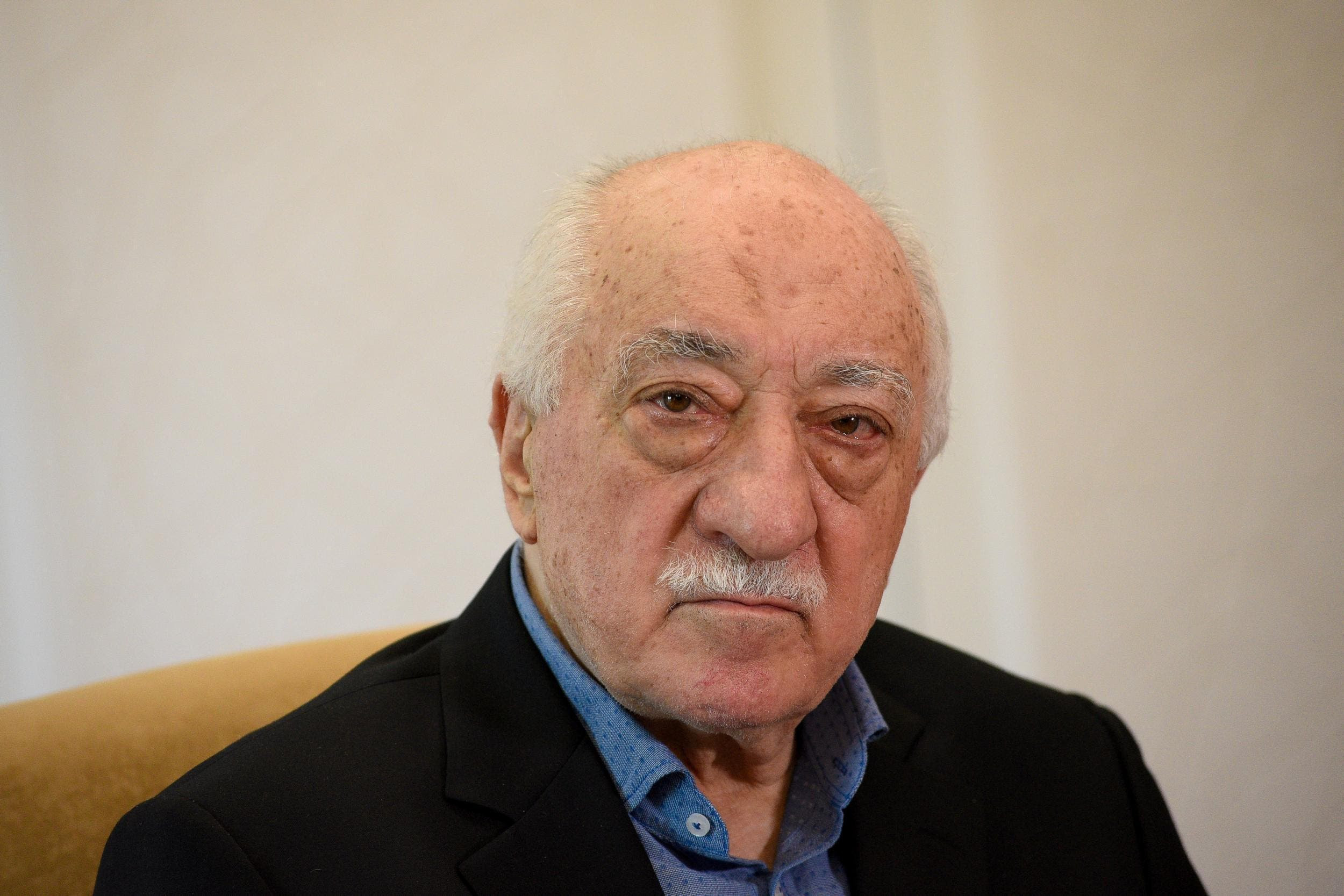
The death of the US-based cleric was announced by Herkul Nagme, a news outlet associated with Gulen, on Monday.
“Our religious leader the great Fethullah Gülen who dedicated his life to Islam and serving humanity has walked on to the horizon of his spirit,” it said on X, adding that he was undergoing treatment at hospital for some time.
Turkish Foreign Minister Hakan Fidan confirmed Gulen’s death at a news conference in Ankara, vowing to continue the fight against the cleric’s group, which is designated as a terrorist organization in Turkey.
“The leader of this dark organization is dead. Our resolve in fighting terrorism remains ongoing. The news of his death will not lead us to complacency,” he said.
State broadcaster TRT announced his death on Monday, calling him “a traitor, an enemy of religion and a terrorist who spent his entire life plotting against” the country.
Gulen's Rise and Exile
Born in 1941, Gulen climbed the ranks of Turkey’s religious bureaucracy to become an influential imam, building his base of followers over decades. However, he went into self-imposed exile in 1999, when he moved from Turkey to the United States and settled in the small, leafy town of Saylorsburg, Pennsylvania.
Supporters described Gulen as a peaceful, moderate cleric who championed interfaith dialogue. His followers, many of whom were lower-middle class pious Muslims disenfranchised by Turkey’s staunch secularist power circles at the time, made up a movement called Hizmet.
Gulen's Movement and its Global Reach
Gulen’s movement has founded schools, free tutoring centers, hospitals and relief agencies that have been credited with addressing some of Turkey’s social problems. Within Turkey, Gulenists also owned TV stations, newspapers, gold mines and at least one bank.
The movement also spawned a global network of schools and universities that operated in more than 100 countries.
When Gulen moved to the US in 1999, his supporters cited medical reasons, while his critics claim he was evading scrutiny for trying to undermine the secular government by establishing a religious one – allegations he denied.
The Erdogan-Gulen Rivalry
When Erdogan took power in 2002, the Hizmet movement threw its support behind the then-prime minister – with many Gulenists among Erdogan’s allies. In fact, it was with their help that Erdogan had previously carried out military purges and shadowy court cases targeting secularist generals and officers.
But the relationship began souring in the early 2010s, triggered by the government trying to shut down Gulenist educational centers and the Gulenists accusing senior administration officials of bribery. Soon their rivalry turned openly hostile, with Erdogan making veiled warnings against “those who are supported by dark circles from inside and outside the country.”
In an interview with CNN in 2014, a top official from Erdogan’s ruling AKP party called the Gulen movement a “fifth column” that had infiltrated the Turkish police force and judiciary.
The government now categorizes the Gulenists as a terrorist organization, called FETO.
The 2016 Coup Attempt and its Aftermath
Then came the attempted coup in 2016, which killed 290 people and injured more than 1,400. After a wave of violence that saw tanks rolling down city roads, the attempted coup was quashed.
Erdogan was quick to point the finger at Gulen, and a crackdown followed. Thousands of people suspected to have links to Gulen were arrested or fired from their jobs. Turkey called on the US to extradite the cleric and the US refusal to do so was one of the main sticking points during a time in which Turkish-American relations hit a new low.
Gulen repeatedly denied the accusations. “As someone who suffered under multiple military coups during the past five decades, it is especially insulting to be accused of having any link to such an attempt. I categorically deny such accusations,” he said at the time.
Gulen's Death: Reactions and Impact
The Turkish government, which continues to view Gulen's movement as a terrorist organization, has vowed to continue its fight against the group. Some analysts believe that Gulen's death could weaken his movement and its influence on Turkish society, while others argue that the organization remains a threat.
The Future of Gulen's Movement
Gulen's death raises questions about the future of his movement, Hizmet. While his influence has been significantly diminished in recent years due to government crackdown and the loss of key assets, the movement remains active in Turkey and abroad. The passing of the movement's founder could lead to internal power struggles and potentially a weakening of the organization. It is unclear how the movement will navigate this transition period.
The US government's stance toward Gulen's movement will also be crucial in shaping its future. Whether the US continues to support the movement or distances itself from it in the wake of Gulen's death remains to be seen. The movement's ability to maintain its presence and influence in Turkey and beyond will be heavily influenced by these factors.
The legacy of Fethullah Gulen is complex and contested. He was a charismatic preacher who inspired millions of followers, but he was also accused of orchestrating a coup attempt that shook Turkey to its core. His death leaves a void in Turkish politics and society that will be felt for years to come.